
Best adjuvant (assist) for chemotherapy | 1+1>487% |
Effectively improve chemotherapy effect, treatment, immunity.
Reduce side effects and recurrence.
Overview / Relation / Abstract / Role / Principle / Action / Mechanism / Function / Work |
Brain Stem Glioma - Childhood: Latest Research
Abstract / Summary / Overview of Apoptosis.
Why do cells undergo apoptosis?
The relationship between cancer cells and apoptosis.
Where are the weaknesses and symptoms of cancer cells?
Are cancer cells aggressive?
Extraordinary Solamargine (Role, Principle, Action, Mechanism, Function, Work)
Solamargine's major function mechanism:
Solamargine vs cancer
Best Chemotherapy Adjuvant. (1+1>478%)
Effectively improve chemotherapy effect and cure.
When cancer cells are less resistant to drugs, chemotherapy becomes more effective.
Extract : https://www.cancer.net/cancer-types
Brain Stem Glioma - Childhood: Latest Research
ON THIS PAGE: You will read about the scientific research being done to learn more about brain stem glioma and how to treat it. Use the menu to see other pages.
Doctors are working to learn more about brain stem glioma, ways to prevent it, how to best treat it, and how to provide the best care to children diagnosed with brain stem glioma. The following areas of research may include new options for patients through clinical trials. Always talk with your child’s doctor about the best diagnostic and treatment options for your child.
Improved imaging and surgery. Imaging techniques are being developed that help the surgeon pinpoint the tumor’s exact location to reduce or prevent damage to the healthy parts of the brain. For example, image-guided stereotaxis allows surgeons to visualize and operate on the brain using 3-dimensional computerized outlines of the brain and the tumor. Along with specialized software, these images help guide the surgeon to the tumor. Tumors that were once considered inoperable can now be removed using this technique. In certain instances, these imaging techniques are also being used to better understand the benefits and risks of using a biopsy to diagnose children with diffuse brain stem glioma.
Improved radiation therapy. Conformal radiation therapy is a way to give high doses of radiation therapy directly to a tumor and not healthy tissue. This technique creates detailed, 3-dimensional maps of the brain and the tumor so doctors know exactly where to deliver the radiation therapy. In addition, drugs designed to enhance the effectiveness of radiation therapy or to slow or stop tumor growth are also being studied.
Molecular features. Other research is focused on evaluating the abnormal molecular features of brain stem glioma cells to better diagnosis and categorize these tumors. These features are found by examining the tumor after a biopsy and may help doctors find treatments that target the tumor based on the specific molecular features (see below).
Targeted therapy. Targeted therapy is a treatment that targets the tumor’s specific genes, proteins, or the tissue environment that contributes to a tumor's growth and survival. This type of treatment blocks the growth and spread of tumor cells while limiting damage to healthy cells. For brain stem glioma, researchers are studying new treatments that target certain molecular features found in the tumor (see above). Learn more about the basics of targeted treatments.
Immunotherapy. Immunotherapy, also called biologic therapy, is designed to boost the body's natural defenses to fight the tumor. It uses materials made either by the body or in a laboratory to improve, target, or restore immune system function. For brain stem glioma, doctors are researching vaccines that may treat the tumor. Learn more about the basics of immunotherapy and cancer vaccines.
New ways to give chemotherapy. The blood-brain barrier, which protects the brain and spinal cord from damaging chemicals, also keeps out many types of chemotherapy. New methods of giving chemotherapy called convection-enhanced delivery are also being studied. This method uses a narrow tube called a catheter that is placed into the brain so chemotherapy can be directed at the tumor.
Palliative care/supportive care. Clinical trials are underway to find better ways of reducing symptoms and side effects of current brain stem glioma treatments to improve comfort and quality of life for patients.
Tissue donation. Some families find that donating tissue feels appropriate as part of the grieving process after their child’s death. Similar to organ donation, tissue donations can help researchers learn more about how tumors change and spread to help develop new treatments for children with brain stem glioma. Talk with your child's doctor for more information about tissue donation.
Abstract / Summary / Overview of Apoptosis.
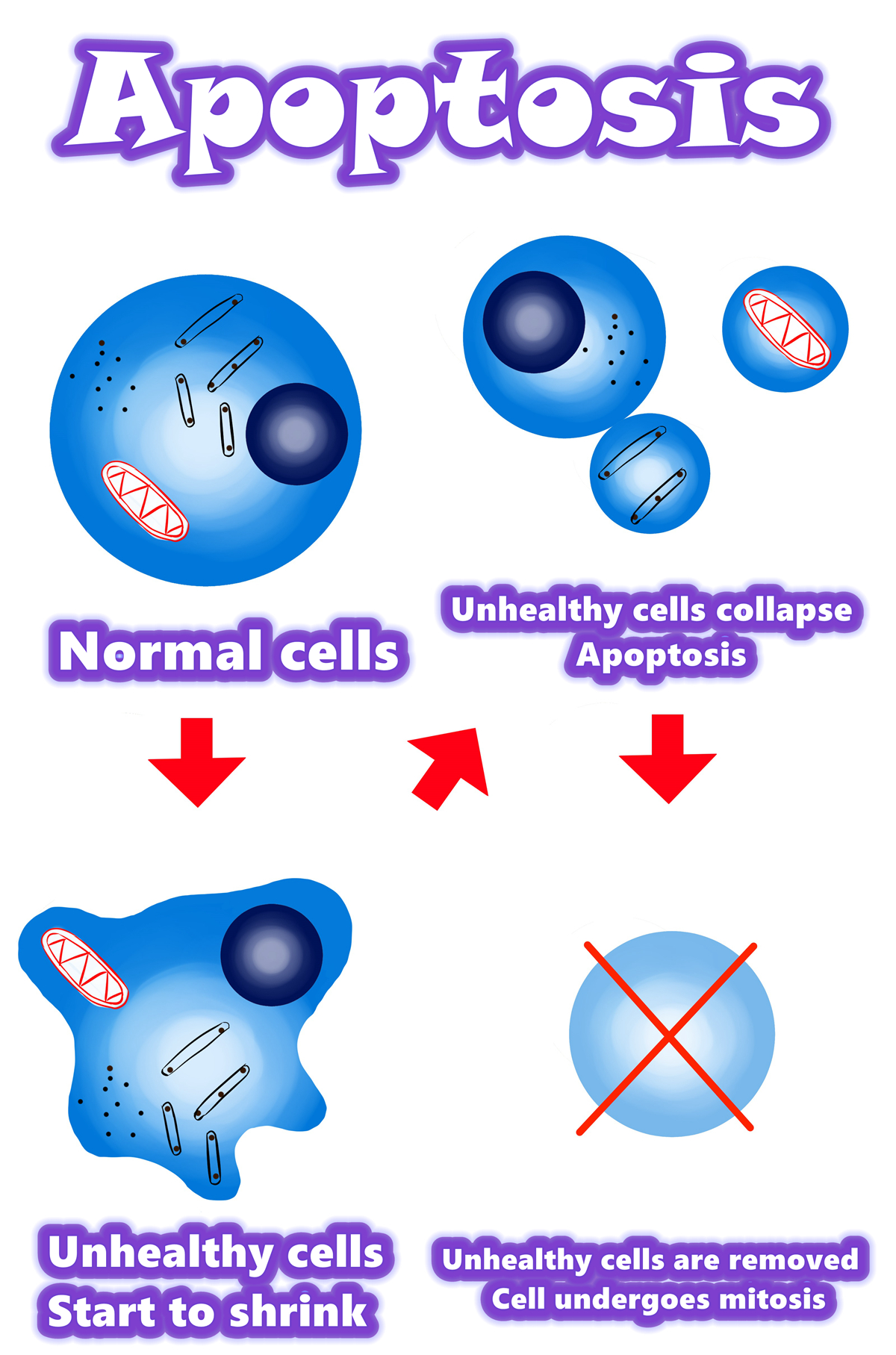
Overview of apoptosis
•Programmed cell death
•Apoptosis is a form of programmed cell death, or “cellular suicide.”
•Apoptosis is different from necrosis, in which cells die due to injury.
•Apoptosis removes cells during development, eliminates potentially cancerous and virus-infected cells, and maintains balance in the body.
Why do cells undergo apoptosis?
- Basically, apoptosis is a general and convenient way to remove cells that should no longer be part of the organism.
- Some cells are abnormal and could hurt the rest of the organism if they survive, such as cells with viral infections or DNA damage.
- Apoptosis is part of development
- In many organisms, programmed cell death is a normal part of development.
The relationship between cancer cells and apoptosis
Apoptosis can eliminate infected or cancerous cells.
When a cell’s DNA is damaged, it will typically detect the damage and try to repair it.
If the damage is beyond repair, the cell will normally send itself into apoptosis, ensuring that it will not pass on its damaged DNA.
When cells have DNA damage but fail to undergo apoptosis, they may be on the road to cancer.
However, “successful” cancer cells successfully evade the process of apoptosis.
This allows them to divide out of control and accumulate mutations (changes in their DNA).
Apoptosis is key to immune function
Apoptosis also plays an essential role in the development and maintenance of a healthy immune system.
Where are the weaknesses and symptoms of cancer cells?
The symptoms of cancer cells are in the nucleus.
The nucleus controls the outer cytoplasm, cell composition, cell viability, etc.
DNA mutations also mutate in the nucleus.
Therefore, to treat cancer cells, we must first enter the nucleus.
Let the “regulatory cell gene” mechanism enter the nucleus to regulate
Are cancer cells aggressive?
After the action of Solamargine, the aggressiveness of cancer cells is alleviated.
So after using Solamargine, many patients feel that I am half better.
Although the tumor does not disappear quickly, patients feel that the degree of aggressiveness is reduced.
Extraordinary Solamargine (Role, Principle, Action, Mechanism, Function, Work).
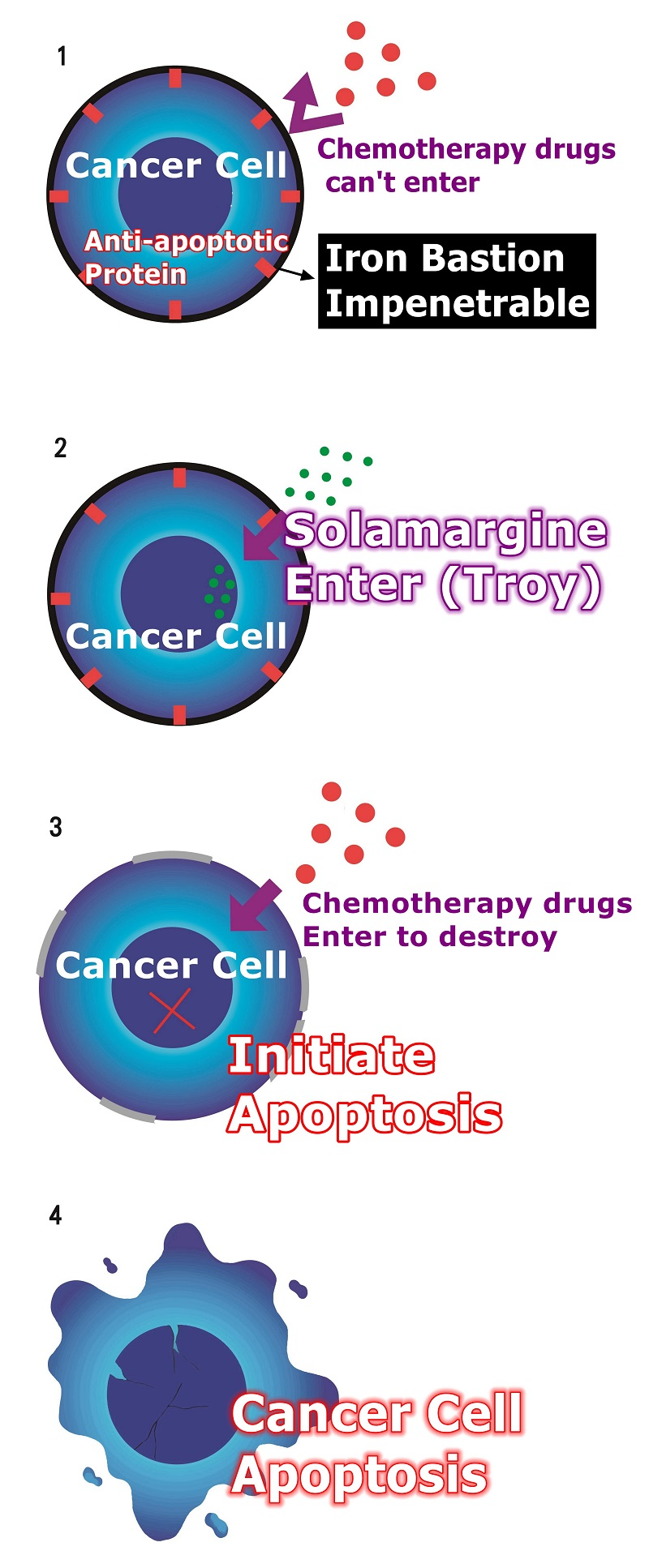
Solamargine's major function mechanism:
When Solamargine enter,
Solamargine activates receptors that are turned off by cancer cells, allowing cancer cells to modulate again.
Solamargine modulates the anti-modulates genes of cancer cells, making cancer cells less resistant.
Reduced drug resistance
When cancer cells are less resistant to drugs, chemotherapy becomes more effective.
Solamargine modulates the mutated genes in cancer cells and then initiates cancer cell apoptosis to achieve anti-cancer effects.
Solamargine combined with which chemotherapy drugs are more effective in treating cancer cells?
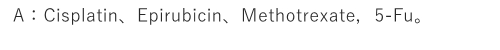
Solamargine vs cancer
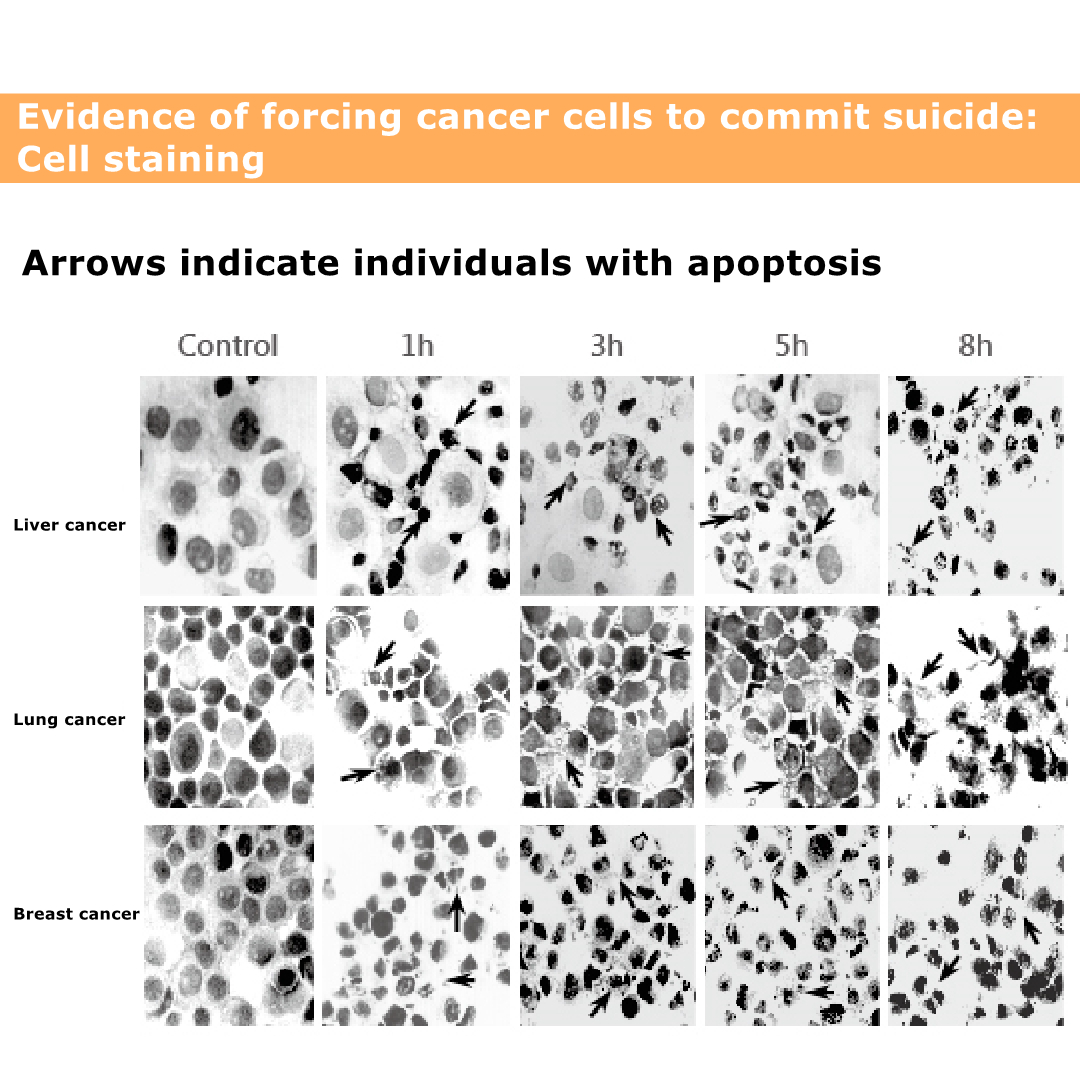
Solamargine vs cancer
The picture shows the death of cancer cells.
The black and black parts are cancer cell nuclei.
Even if the nucleus ruptures, the cancer cells will die.
The figure shows that cancer cells can cause death.
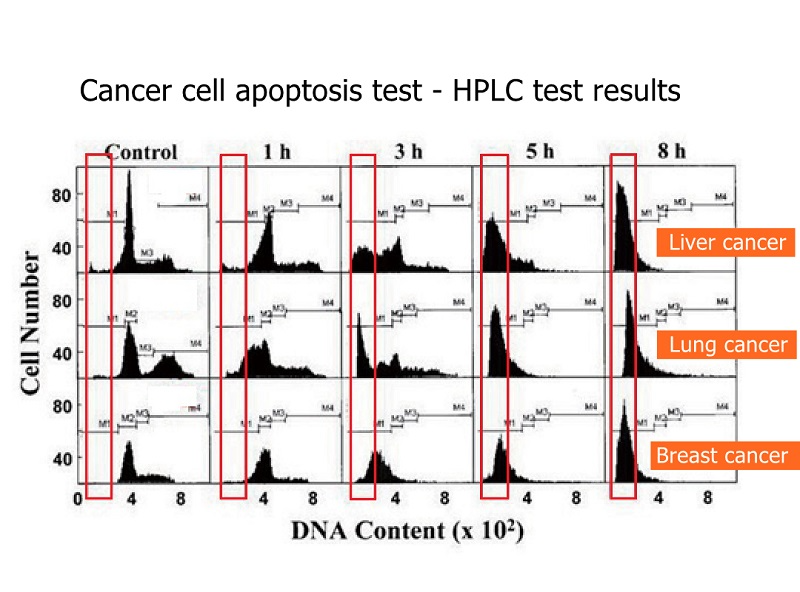
The figure shows that cancer cells can cause death.
The figure shows that the death of lung cancer cells is relatively slow, and it will not be obvious until eight hours later.
The figure shows that the death of liver cancer cells is very obvious, even more obvious in eight hours.
The graph shows that breast cancer cells die faster. It was obvious from the beginning that breast cancer is easy to treat, and patients with breast cancer need not worry.
Best Chemotherapy Adjuvant. (1+1>487%)
Effectively improve chemotherapy effect and treatment.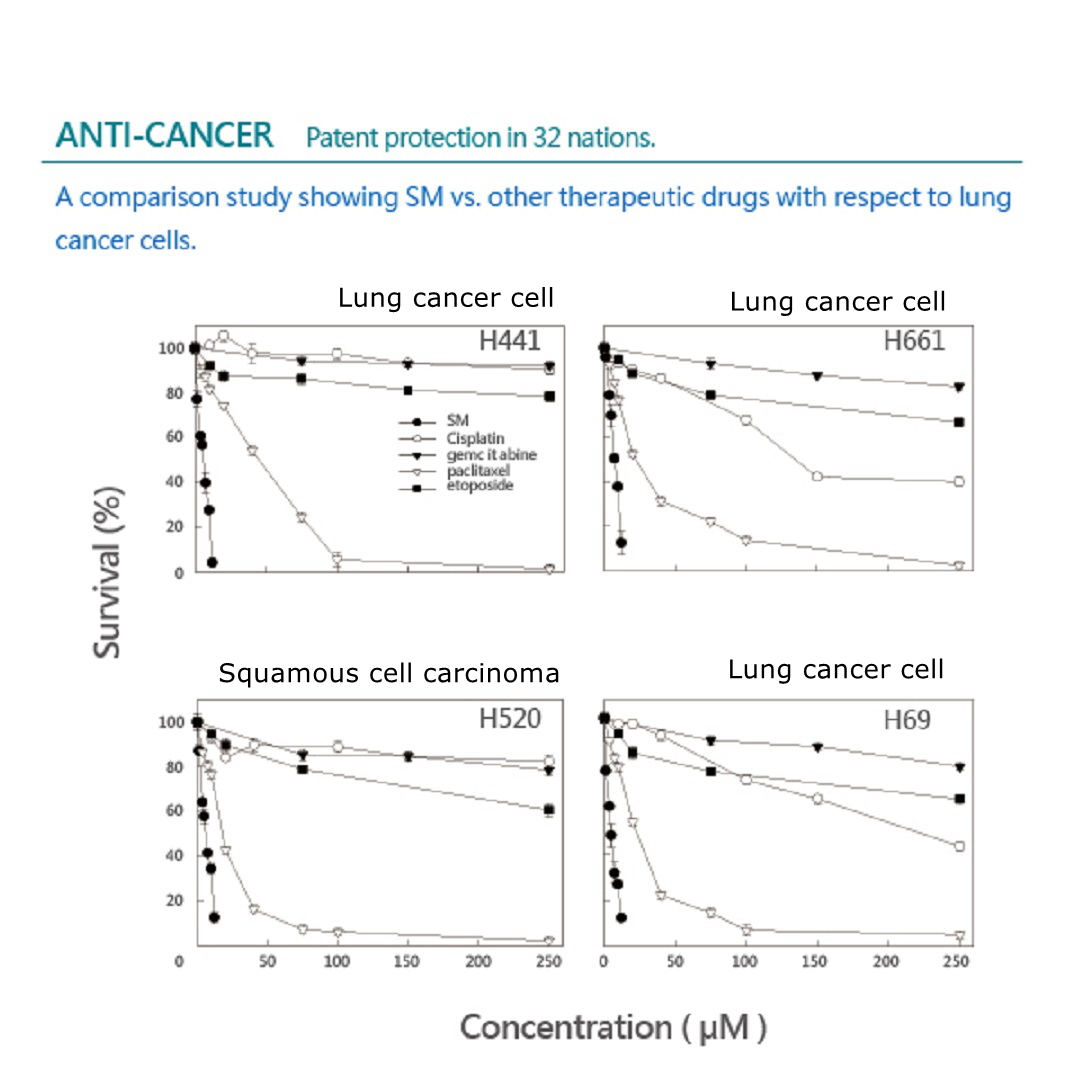
ANTI-CANCER
Patent protection in 32 nations.
A comparison study showing Solamargine vs. other therapeutic drugs with respect to lung cancer cells.
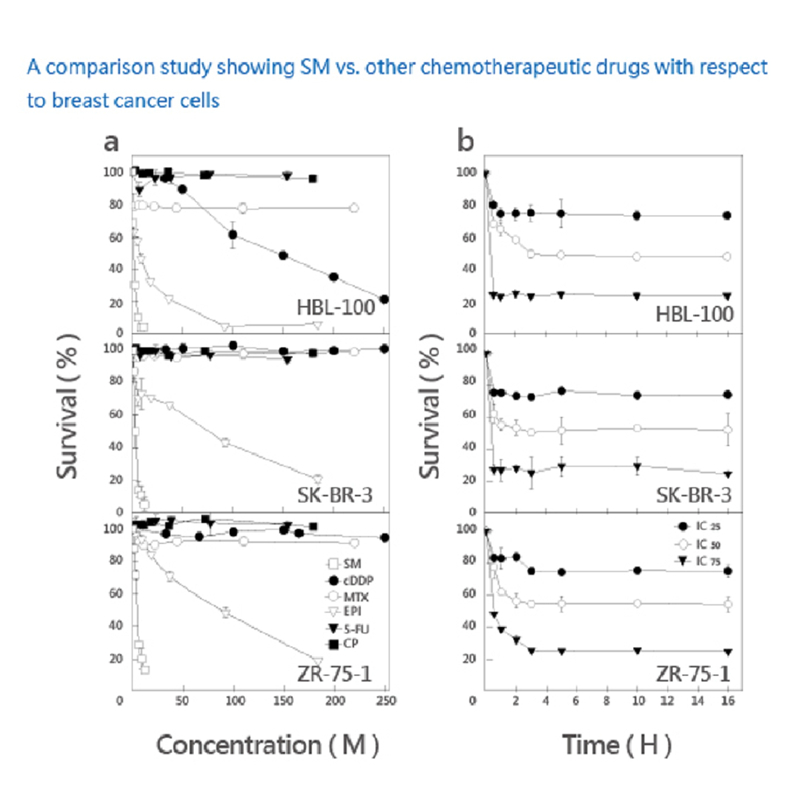 A comparison study showing Solamargine vs. other chemotherapeutic drugs with respect to breast cancer cells.
A comparison study showing Solamargine vs. other chemotherapeutic drugs with respect to breast cancer cells.
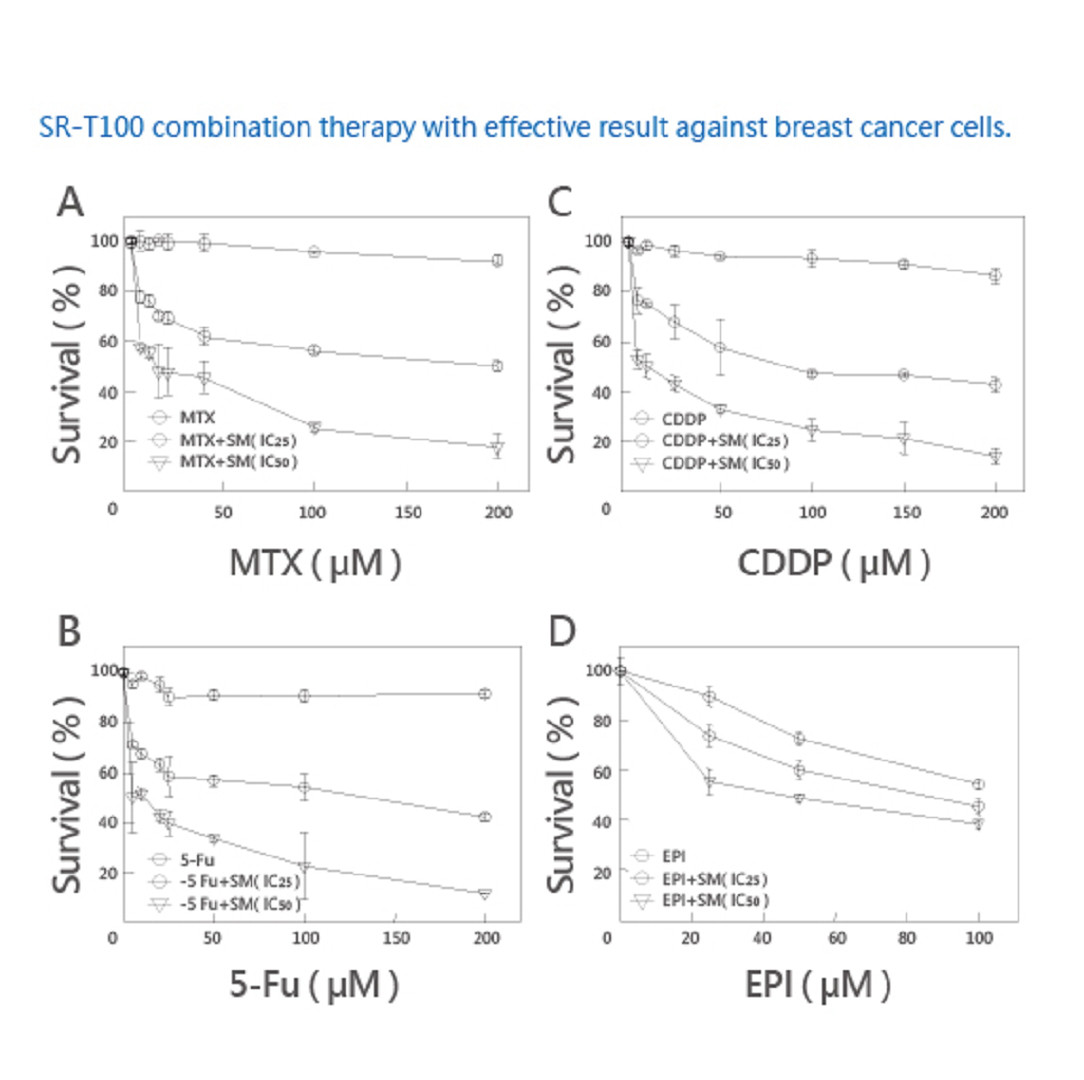
SR-T100 combination therapy with effective result against breast cancer cells.
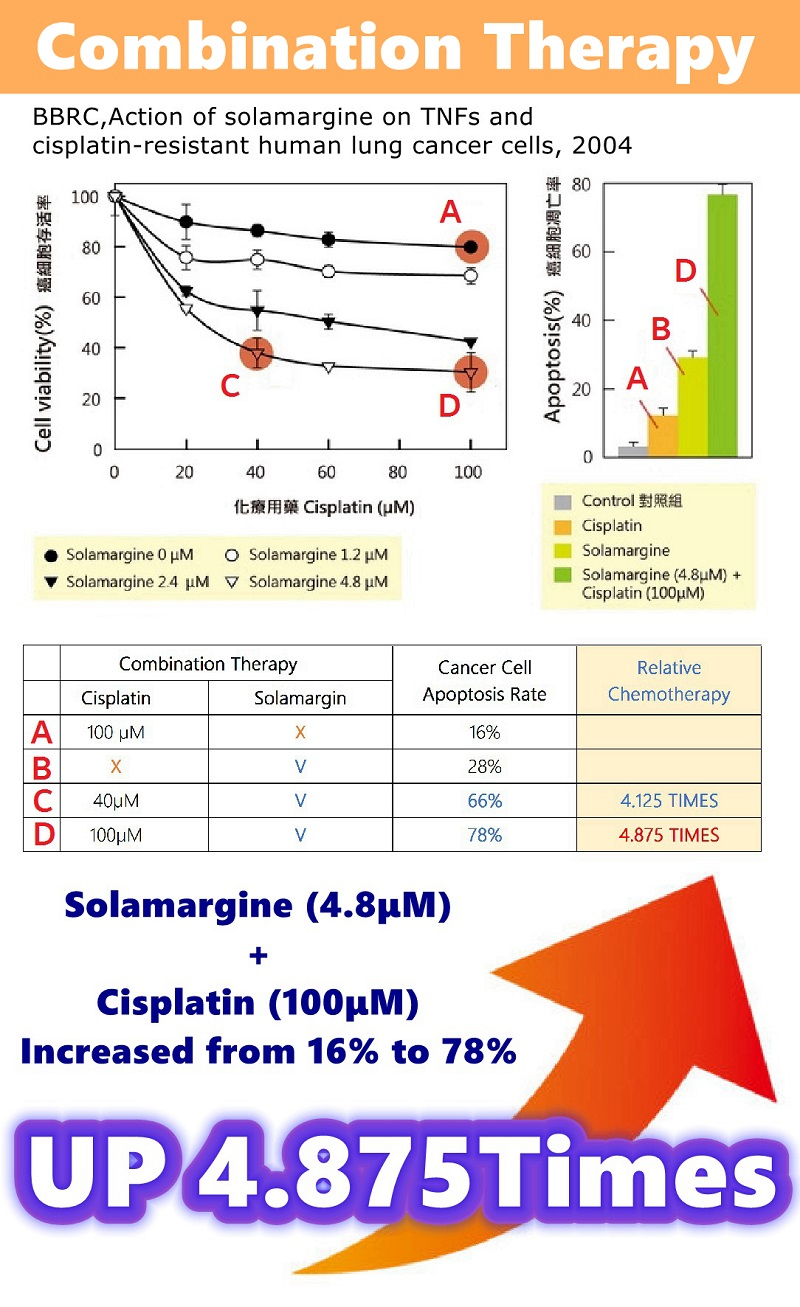
Combination Therapy | Research results for lung cancer cells.
A. Chemotherapy (100μM), 16% of cancer cell apoptosis.
B. Alone SM (4.8μM), 28% of cancer cell apoptosis.
C. SM (4.80μM) + Chemotherapy (40μM), 66% of cancer cells apoptosis.
D. SM (4.80μM) + Chemotherapy (100μM), 78% of cancer cell apoptosis.
SM has a clearing effect better than Chemotherapy.
The combined treatment of Solamargine and Chemotherapy significantly increased the apoptosis of lung cancer cells.
SM (4.8μM) + Chemotherapy (40μM), increased from 16% to 66% (up to 4.125 times).
SM (4.8μM) + Chemotherapy (100μM), increased from 16% to 78% (up to 4.875 times).
Reorganized from: BBRC. Action of Solamargine on TNFs and drug-resistant human lung cancer cells 2004.
The best solution for cancer cells.
