Best Combination Chemotherapy Therapy for Pancreatic cancer (PC). | 1+1> 487%
Effectively improve chemotherapy effect, treatment, immunity.
Reduce side effects and recurrence.
Combination Therapy. | Overview / Relationship / Abstract / Role / Principle / Action / Mechanism / Function / Work.
Abstract / Summary / Overview of Pancreatic cancer (PC).
Abstract / Summary / Overview of Apoptosis.
Role, Principle, Action, Mechanism, Function, Work of Solamargine.
Best Combination Chemotherapy Therapy for Pancreatic cancer (PC).
1. Fe3O4-Solamargine induces apoptosis and inhibits metastasis of pancreatic cancer cells.
2. Solamargine induces apoptosis and sensitizes breast cancer cells to cisplatin.
3. Action of Solamargine on TNFs and cisplatin-resistant human lung cancer cells.
Abstract / Summary / Overview of Pancreatic cancer (PC).
Pancreatic cancer (PC) originates in the pancreas.
The most common type of Pancreatic cancer (PC) is pancreatic ductal adenocarcinoma, which accounts for ~85% of Pancreatic cancer (PC) case, and the incidence of Pancreatic Cancer (PC) is increasing.
Pancreatic Cancer (PC) is prone to metastasis in the early stages.
Although the development of surgical techniques and novel drugs is progressing, the 5-year survival rate remains approximately 6%.
Surgery, radiotherapy, and chemotherapy remain the three main traditional tumor therapy methods.
A major challenge in treating Pancreatic cancer (PC) is the poor prognosis for advanced and recurrent cases.
Although chemotherapy is the main approach used to treat advanced and recurrent PC cases, its clinical performance is largely limited by various factors such as a relatively low response rate, drug resistance, and various adverse effects that substantially impact the quality of life (QOL) of Pancreatic Cancer (PC) patients.
However, it is difficult to achieve satisfactory outcomes by applying the traditional treatment methods, as surgery may result in trauma, and radiotherapy and chemotherapy may lead to severe side effects.
Although recent advances in the understanding of the biological characteristics of this illness and multidisciplinary therapeutic approaches, such as individuated chemotherapy, targeted therapies, immune approaches, and improved supportive care, the outcome remains dismal for patients with advanced disease.
One approach to overcome this problem is the development of new agents that can be used in combination with existing chemotherapeutics to yield better results than chemotherapeutics alone.
Therefore, searching for more effective alternative treatment strategies to strengthen the therapeutic efficacy with negligible side effects is urgently needed.
Accumulating evidence suggests that many natural products, including extracts and isolated chemicals, have the potential to interact with multiple targets in the signaling pathways that regulate cancer progression.
Natural phytochemicals derived from medicinal plants have gained significant recognition in the control of carcinogenesis and are considered as a novel approach in the prevention and treatment of cancer.
A large number of investigators have now reported that Solamargine induces cell cycle arrest and apoptosis in a wide variety of cancer cells, such as basal cell carcinoma, squamous cell carcinoma, melanoma, colorectal cancer, bladder cancer, oral epidermoid carcinoma, myelogenous leukemia, prostate cancer, breast cancer, lung cancer, endometrial cancer, pancreatic cancer, gastric carcinoma, renal cancer, uterine cancer, mesothelioma, glioblastoma, osteosarcoma, Pancreatic cancer (PC).
Apoptosis or programmed cell death plays a significant role in the growth regulation of normal and neoplastic tissues since it balances cell proliferation.
Apoptosis usually occurs in a well-designed sequence of morphological events mediated by intrinsic and extrinsic pathways and has been demonstrated to activate the programmed cell death pathway to exert anticancer functions.
Abstract / Summary / Overview of Apoptosis.

•Programmed cell death.
•Apoptosis is a form of programmed cell death, or “cellular suicide.”
•Apoptosis is different from necrosis, in which cells die due to injury.
•Apoptosis removes cells during development, eliminates potentially cancerous and virus-infected cells, and maintains balance in the body.
Why do cells undergo apoptosis?
Apoptosis is a general and convenient way to remove cells that should no longer be part of the organism.
Some cells are abnormal and could hurt the rest of the organism if they survive, such as cells with viral infections or DNA damage.
Apoptosis is part of the development.
In many organisms, programmed cell death is a normal part of development.
The relationship between cancer cells and apoptosis.
Apoptosis can eliminate infected or cancerous cells.
When a cell’s DNA is damaged, it will typically detect the damage and try to repair it.
If the damage is beyond repair, the cell will normally send itself into apoptosis, ensuring that it will not pass on its damaged DNA.
When cells have DNA damage but fail to undergo apoptosis, they may be on the road to cancer.
However, “successful” cancer cells successfully evade the process of apoptosis.
This allows them to divide out of control and accumulate mutations (changes in their DNA).
Apoptosis is key to immune function.
Apoptosis also plays an essential role in the development and maintenance of a healthy immune system.
Apoptosis or programmed cell death plays a significant role in the growth regulation of normal and neoplastic tissues since it balances cell proliferation.
Cells undergoing apoptosis usually present cell shrinkage, chromatin condensation, nuclear fragmentation, and apoptotic bodies.
Apoptosis usually occurs in a well-designed sequence of morphological events mediated by intrinsic and extrinsic pathways and has been demonstrated to activate the programmed cell death pathway to exert anticancer functions.
Numerous antitumor drugs are known to trigger cell death by inducing apoptosis.
Where are the weaknesses and symptoms of cancer cells?
The symptoms of cancer cells are in the nucleus.
The nucleus controls the outer cytoplasm, cell composition, cell viability, etc.
DNA mutations also mutate in the nucleus.
Therefore, to treat cancer cells, we must first enter the nucleus.
Let the “regulatory cell gene” mechanism enter the nucleus to regulate
Are cancer cells aggressive?
After the action of Solamargine, the aggressiveness of cancer cells is alleviated.
So after using Solamargine, many patients feel that I am half better.
Although the tumor does not disappear quickly, patients feel that the degree of aggressiveness is reduced.
Role, Principle, Action, Mechanism, Function, Work of Solamargine.
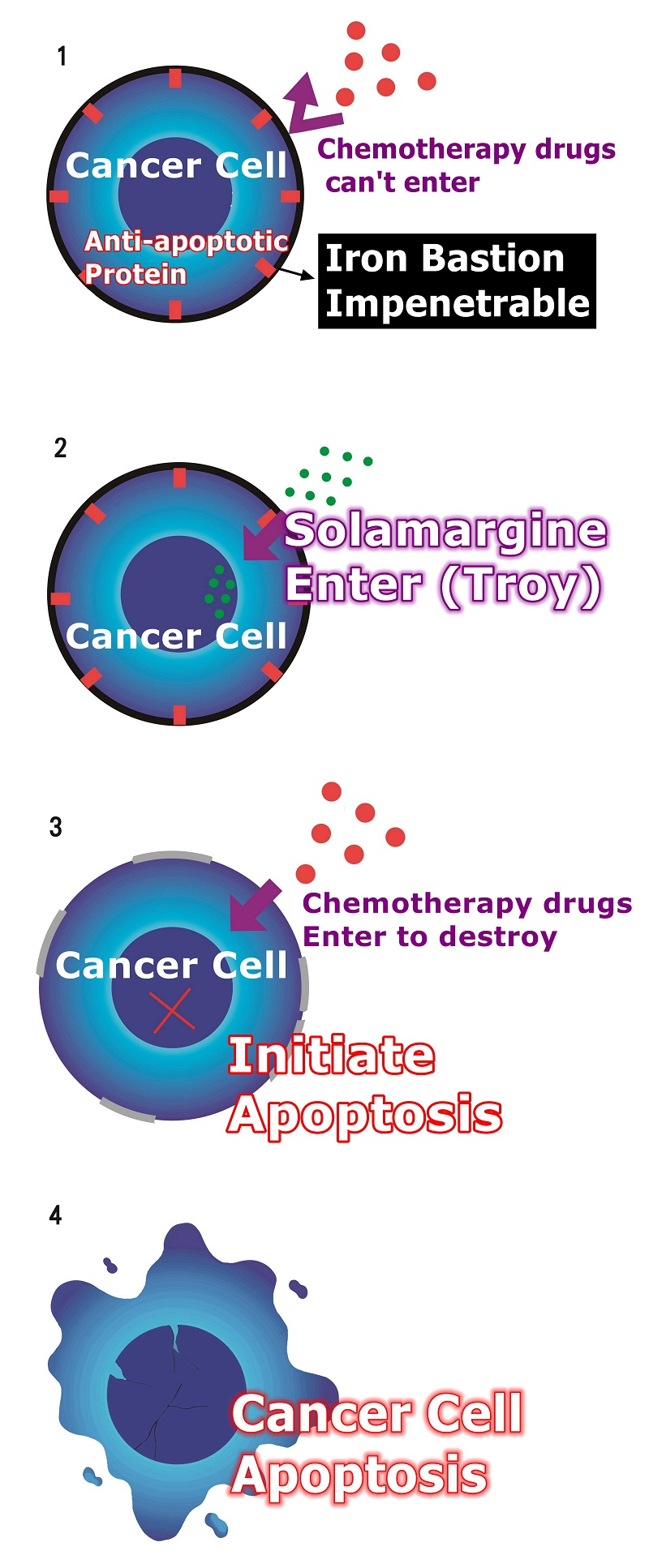
SM major function mechanism, role, principle, action, function, work:
When Solamargine enter,
Solamargine activates receptors that are turned off by cancer cells, allowing cancer cells to modulate again.
Solamargine modulates the anti-modulates genes of cancer cells, making cancer cells less resistant.
Reduced drug resistance (Reduce resistance).
When cancer cells are less resistant to drugs, chemotherapy becomes more effective.
Solamargine modulates the mutated genes in cancer cells and then initiates cancer cell apoptosis to achieve anti-cancer effects.
More specifically, it was shown the Solamargine, in particular, induced apoptosis (target) in cancer cells but not normal cells.
Solamargine combined with which chemotherapy drugs are more effective in treating cancer cells?
A: Cisplatin (CDDP), Cranberry, Methotrexate, 5-Fu.
Best Combination Chemotherapy Therapy for Pancreatic cancer (PC). | 1+1> 487%
Effectively improve chemotherapy effect, treatment, immunity | Reduce side effects and recurrence.
Combination Therapy | Overview / Relationship / Abstract / Role / Principle / Action / Mechanism / Function / Work.

Solamargine vs cancer
ANTI-CANCER
Patent protection in 32 nations.
A comparison study showing Solamargine vs. other therapeutic drugs with respect to lung cancer cells.
Solamargine, the typical metabolites of solanum lycocarpum fruit glycoalkaloid extract from traditional herbal medicine, demonstrated not only anti-viral, anti-inflammatory but also antiproliferative activity against the multiple types of human cancers including Liver.
Solamargine, isolated from Solanum incanum herb, displayed superior cytotoxicity in four human lung cancer cell lines.
Solamargine not only inhibits cell growth of lung cancer (SCLC, NSCLC), Pancreatic cancer (PC), Liver cancer, Melanoma, and Cholangiocarcinoma but also enhances the cytotoxicity of chemotherapy agents such as cisplatin, doxorubicin, and docetaxel.

Arrows indicate individuals with apoptosis.
The picture shows the death of cancer cells.
The black and black parts are cancer cell nuclei.
Even if the nucleus ruptures, the cancer cells will die.
The figure shows that cancer cells can cause death.

The figure shows that cancer cells can cause death.
The figure shows that the death of lung cancer cells is relatively slow, and it will not be obvious until eight hours later.
The figure shows that the death of Liver Cancer cells is very obvious, even more obvious in eight hours.
The graph shows that Breast Cancer cells die faster. It was obvious from the beginning that Breast Cancer is easy to treat, and patients with Breast Cancer need not worry.
1. Fe3O4-Solamargine induces apoptosis and inhibits metastasis of pancreatic cancer cells.
2. Solamargine induces apoptosis and sensitizes breast cancer cells to cisplatin.
3. Action of Solamargine on TNFs and cisplatin-resistant human lung cancer cells.
Results
1. The current study confirms the antiproliferative anticancer activity of Solamargine isolated from the methanolic extract of the fruit peels of Solanum melongena against Pancreatic cancer cell lines of susceptibility.
2. The Proliferation of Pancreatic cancer cells is inhibited by Solamargine.
3. Solamargine potentiated cisplatin and doxorubicin-induced cytotoxicity in cancer cells but had no effect on normal human cells.
4. Integrated treatment of Solamargine with cisplatin and doxorubicin may substantially reduce the required dose of cisplatin and doxorubicin required to achieve the same tumor-suppression efficiency, thereby improving the quality of life (QOL) of cancer patients during chemotherapy.
5. Solamargine cotreatment potentiated cisplatin- and doxorubicin-induced cytotoxicity in cancer cells.
6. Solamargine can be used in novel integrated chemotherapy with cisplatin and doxorubicin to improve tumor-suppression efficiency in cancer treatment.
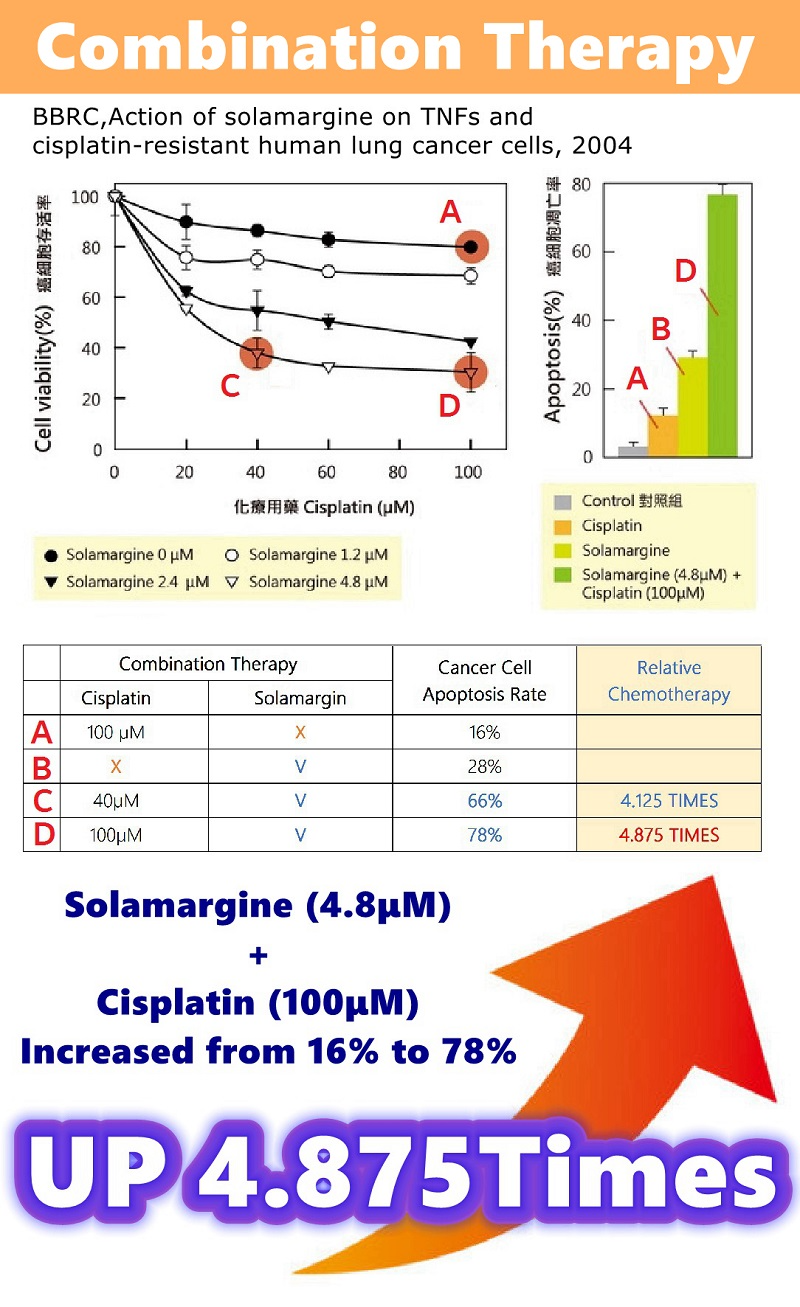
Combination Therapy | Research results for lung cancer cells.
A. Cisplatin (100μM), 16% of cancer cell apoptosis.
B. Alone SM (4.8μM), 28% of cancer cell apoptosis.
C. SM (4.8μM) + Cisplatin (40μM), 66% of cancer cells apoptosis.
D. SM (4.8μM) + Cisplatin (100μM), 78% of cancer cell apoptosis.
Solamargine has a clearing effect better than Cisplatin.
The combined treatment of Solamargine and Cisplatin significantly increased the apoptosis of lung cancer cells.
SM (4.8μM) + Cisplatin (40μM), increased from 16% to 66% (up to 4.125 times).
SM (4.8μM + Cisplatin (100μM), increased from 16% to 78% (up to 4.875 times).
Reorganized from: BBRC. Action of Solamargine on TNFs and drug-resistant human lung cancer cells 2004.
All excerpted from: https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/
advanced pancreatic cancer
alex trebek pancreatic cancer treatment
best pancreatic cancer treatment centers
Cisplatin pancreatic cancer
early signs of pancreatic cancer
Immunotherapy for pancreatic cancer
israel pancreatic cancer treatment
Keytruda pancreatic cancer
Latest pancreatic cancer treatment
new pancreatic cancer treatment
Pancreas cancer
Pancreas cancer diagnosis
pancreatic
pancreatic cancer
Pancreatic cancer - uptodate
Pancreatic cancer approved drugs
pancreatic cancer article
pancreatic cancer ca19-9
pancreatic cancer causes
pancreatic cancer chemo
pancreatic cancer chemotherapy
pancreatic cancer diagnosis
Pancreatic cancer diagnosis
Pancreatic cancer drug
Pancreatic cancer ICD 10
Pancreatic cancer ICD 9
Pancreatic cancer ICD-10
Pancreatic cancer ICD-9
Pancreatic cancer metastasis
pancreatic cancer miracle cure
pancreatic cancer prognosis
Pancreatic cancer stage 4
Pancreatic cancer Staging
pancreatic cancer survival rate
pancreatic cancer survival rates
pancreatic cancer symptoms
pancreatic cancer symptoms female
pancreatic cancer symptoms male
Pancreatic cancer target
Pancreatic cancer targeted therapy
pancreatic cancer therapy
pancreatic cancer treatment
Pancreatic cancer treatment guideline
pancreatic cancer treatment guidelines
pancreatic cancer treatment options
pancreatic cancer treatment stage 4
Pancreatic cancer tumor marker
Pancreatic cancer uptodate
pancreatic cancer wiki
pancreatic metastatic cancer
pancreatic tail cancer treatment
Pancreatic tumor
Pembrolizumab for pancreatic cancer
prevention of pancreatic cancer
Prostate cancer
signs of pancreatic cancer
stage 4 pancreatic cancer
Targeted therapy for pancreatic cancer
what are the early warning signs of pancreatic cancer
what causes pancreatic cancer
What happens if pancreas is removed
what is the latest treatment for pancreatic cancer
what is the most effective treatment for pancreatic cancer
when to stop chemo for pancreatic cancer