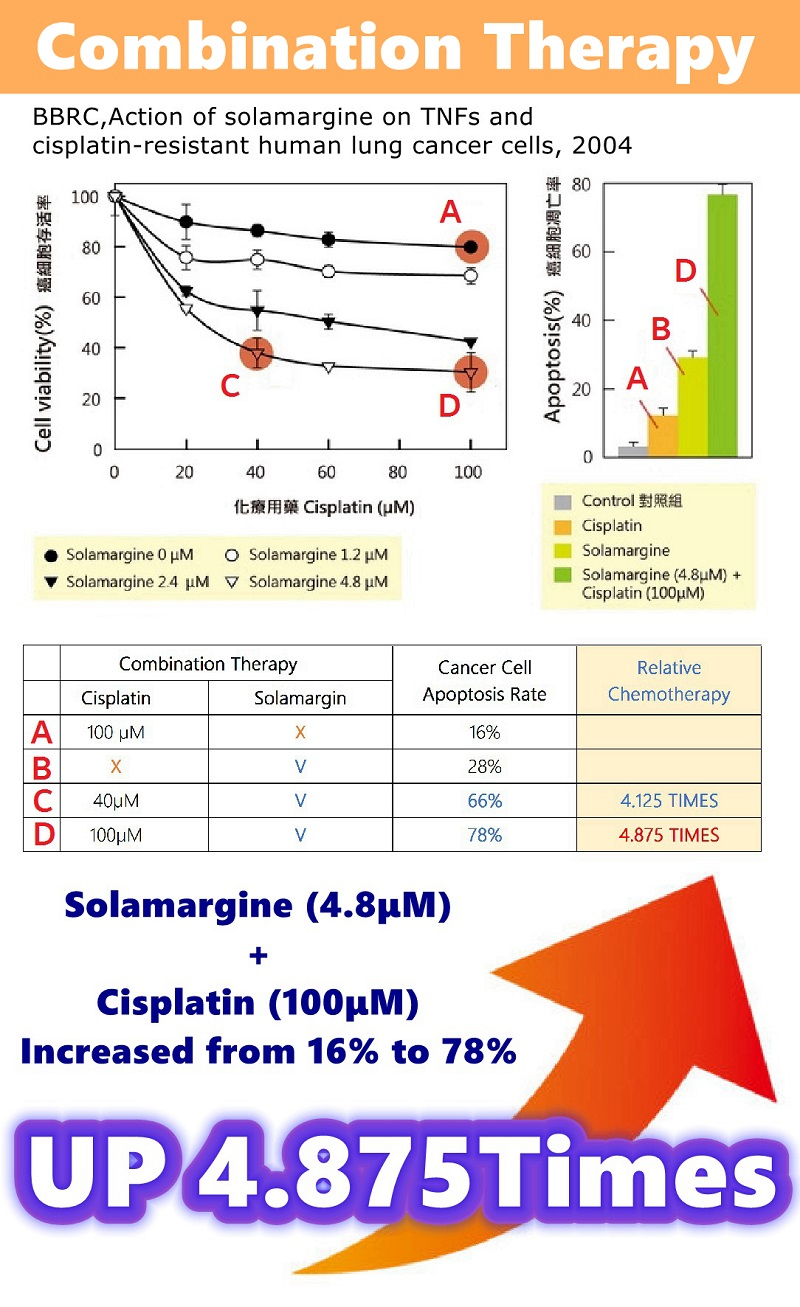
Best adjuvant (assist) for chemotherapy | 1+1>487% |
Effectively improve chemotherapy effect, treatment, immunity |
Reduce side effects and recurrence |
Overview / Relation / Abstract / Role / Principle / Action / Mechanism / Function / Work |
Abstract / Summary / Overview of Apoptosis
Why do cells undergo apoptosis?
The relationship between cancer cells and apoptosis
Where are the weaknesses and symptoms of cancer cells?
Are cancer cells aggressive?
Extraordinary Solamargine (Role, Principle, Action, Mechanism, Function, Work)
Solamargine's major function mechanism:
Solamargine vs cancer
Best Chemotherapy Adjuvant (1+1>478%)
Effectively improve chemotherapy effect and cure.
When cancer cells are less resistant to drugs, chemotherapy becomes more effective.
Childhood Supratentorial Primitive Neuroectodermal Tumors and Pineoblastoma Treatment
Childhood supratentorial primitive neuroectodermal tumors start in the cerebrum. The cerebrum, which is at the top of the head, is the largest part of the brain. The cerebrum controls thinking, learning, problem solving, speech, emotions, reading, writing, and voluntary movement. Childhood supratentorial primitive neuroectodermal tumors are also called cerebral neuroblastomas or cerebral medulloblastomas.
Pineoblastoma form in or near the pineal gland. The pineal gland is a tiny organ in the brain that produces melatonin, a substance that helps control our sleeping and waking cycle.
Although cancer is rare in children, brain tumors are the most common type of childhood cancer other than leukemia and lymphoma.
This summary refers to the treatment of primary brain tumors (tumors that begin in the brain). Treatment of metastatic brain tumors, which are tumors formed by cancer cells that begin in other parts of the body and spread to the brain, is not discussed in this summary.
Brain tumors can occur in both children and adults; however, treatment for children may be different than treatment for adults. See the following PDQ treatment summaries for more information:
Childhood Brain and Spinal Cord Tumors Treatment Overview
The cause of most childhood brain tumors is unknown.
The symptoms of childhood supratentorial primitive neuroectodermal tumors and pineoblastoma vary and often depend on the child’s age, where the tumor is located, and the size of the tumor.
The following symptoms and others may be caused by a supratentorial primitive neuroectodermal tumor or a pineoblastoma. Other conditions may cause the same symptoms. A doctor should be consulted if any of these problems occur:
Weakness or change in sensation on one side of the body.
Morning headache or headache that goes away after vomiting.
Nausea and vomiting.
Unusual sleepiness or change in energy level.
Change in personality or behavior.
Unexplained weight loss or weight gain.
Extract : https://www.cancer.gov/rare-brain-spine-tumor/tumors/pnet
Primitive Neuro-Ectodermal Tumors (PNET) Diagnosis and Treatment
PNETs are primary central nervous system (CNS) tumors. This means they begin in the brain or spinal cord. PNET is a term that stands for a group of tumors, and these tumors are currently being reclassified and given other specific names based on their molecular features.
To get an accurate diagnosis, a piece of tumor tissue will be removed during surgery, if possible. A neuropathologist should then review the tumor tissue.
What are the grades of PNETs?
Primary CNS tumors are graded based on the tumor location, tumor type, extent of tumor spread, genetic findings, the patient’s age, and tumor remaining after surgery, if surgery is possible.
The group of tumors, formerly known as PNETs, are Grade IV tumors. This means they are malignant (cancerous) and fast-growing. These are tumor types that belong to this group:
- Medulloepithelioma
- CNS neuroblastoma
- CNS ganglioneuroblastoma
- Embryonal tumor with multilayered rosettes and other unspecified embryonal tumors
Abstract / Summary / Overview of Apoptosis
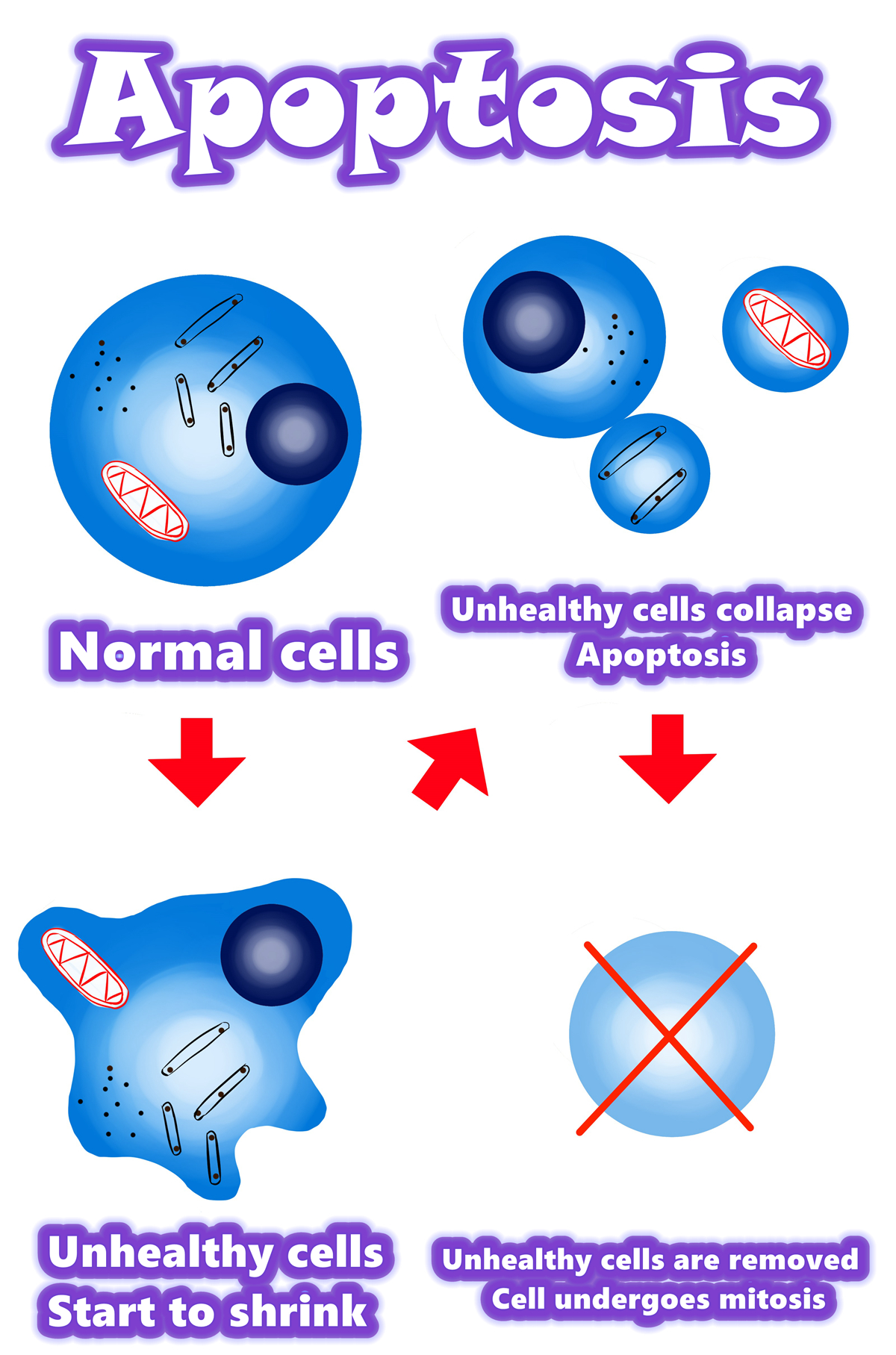
Overview of apoptosis
•Programmed cell death.
•Apoptosis is a form of programmed cell death, or “cellular suicide.”
•Apoptosis is different from necrosis, in which cells die due to injury.
•Apoptosis removes cells during development, eliminates potentially cancerous and virus-infected cells, and maintains balance in the body.
Why do cells undergo apoptosis?
- Basically, apoptosis is a general and convenient way to remove cells that should no longer be part of the organism.
- Some cells are abnormal and could hurt the rest of the organism if they survive, such as cells with viral infections or DNA damage.
- Apoptosis is part of development.
- In many organisms, programmed cell death is a normal part of development.
The relationship between cancer cells and apoptosis.
Apoptosis can eliminate infected or cancerous cells.
When a cell’s DNA is damaged, it will typically detect the damage and try to repair it.
If the damage is beyond repair, the cell will normally send itself into apoptosis, ensuring that it will not pass on its damaged DNA.
When cells have DNA damage but fail to undergo apoptosis, they may be on the road to cancer.
However, “successful” cancer cells successfully evade the process of apoptosis.
This allows them to divide out of control and accumulate mutations (changes in their DNA).
Apoptosis is key to immune function.
Apoptosis also plays an essential role in the development and maintenance of a healthy immune system.
Where are the weaknesses and symptoms of cancer cells?
The symptoms of cancer cells are in the nucleus.
The nucleus controls the outer cytoplasm, cell composition, cell viability, etc.
DNA mutations also mutate in the nucleus.
Therefore, to treat cancer cells, we must first enter the nucleus.
Let the “regulatory cell gene” mechanism enter the nucleus to regulate.
Are cancer cells aggressive?
After the action of Solamargine, the aggressiveness of cancer cells is alleviated.
So after using Solamargine, many patients feel that I am half better.
Although the tumor does not disappear quickly, patients feel that the degree of aggressiveness is reduced.
Extraordinary Solamargine (Role, Principle, Action, Mechanism, Function, Work).
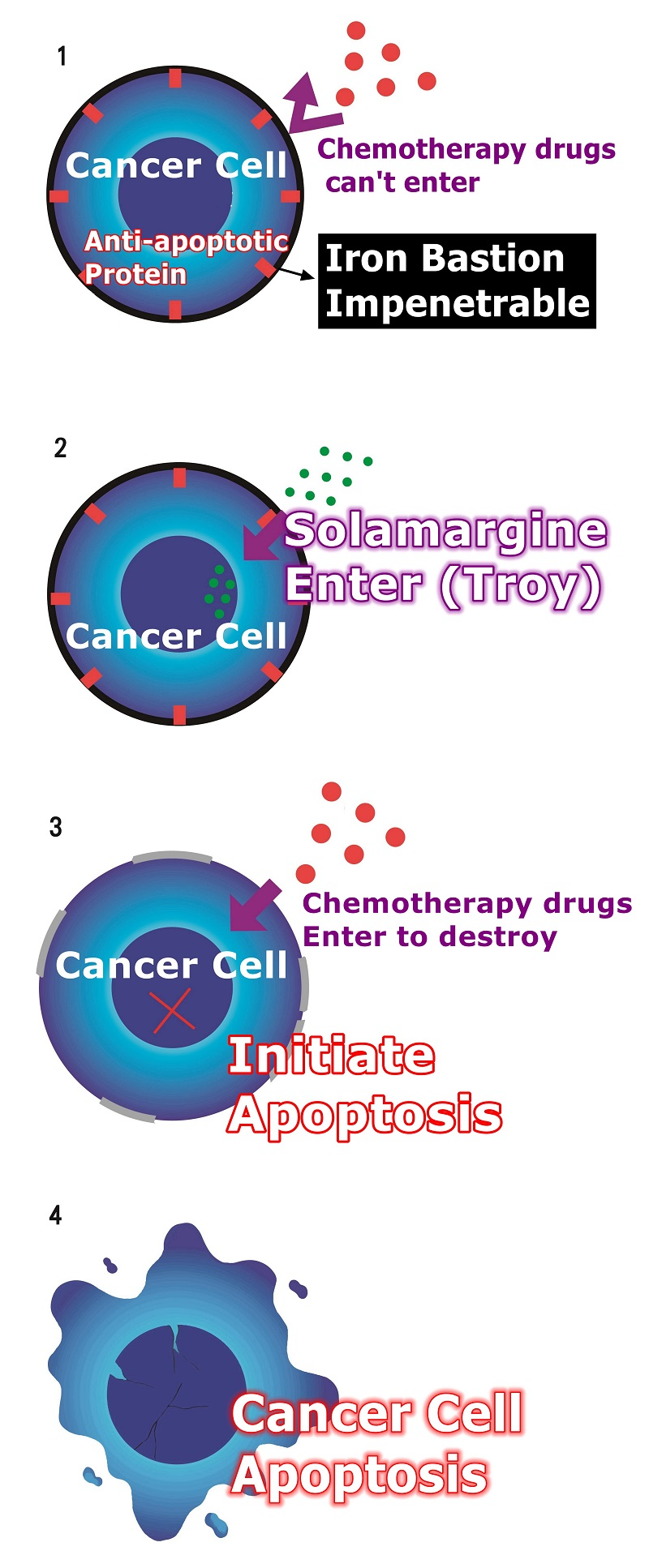
Solamargine's major function mechanism:
When Solamargine enter,
Solamargine activates receptors that are turned off by cancer cells, allowing cancer cells to modulate again.
Solamargine modulates the anti-modulates genes of cancer cells, making cancer cells less resistant.
Reduced drug resistance.
When cancer cells are less resistant to drugs, chemotherapy becomes more effective.
Solamargine modulates the mutated genes in cancer cells and then initiates cancer cell apoptosis to achieve anti-cancer effects.
Solamargine combined with which chemotherapy drugs are more effective in treating cancer cells?
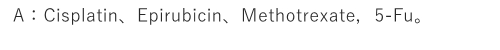
Solamargine vs cancer
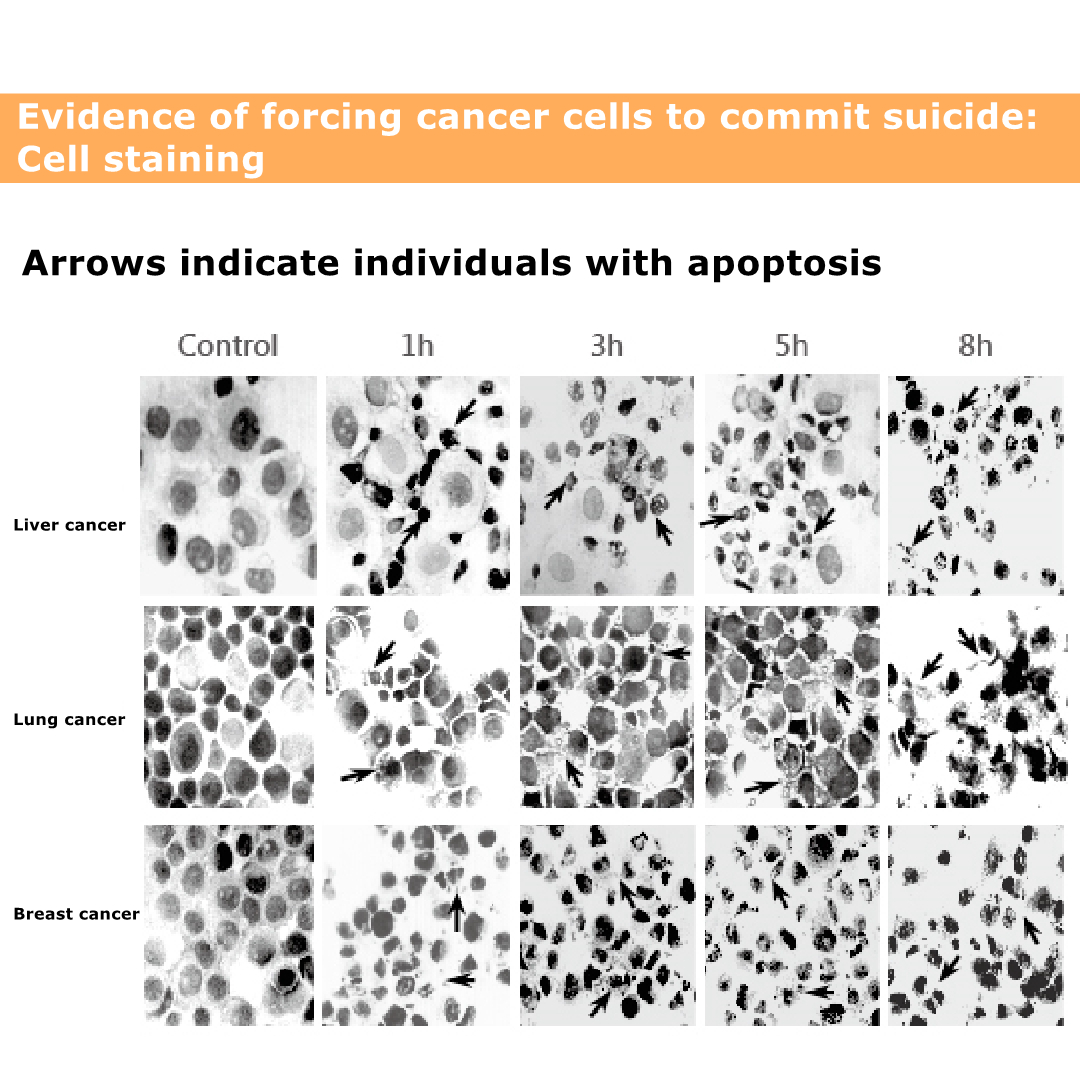
Solamargine vs cancer
The picture shows the death of cancer cells.
The black and black parts are cancer cell nuclei.
Even if the nucleus ruptures, the cancer cells will die.
The figure shows that cancer cells can cause death.
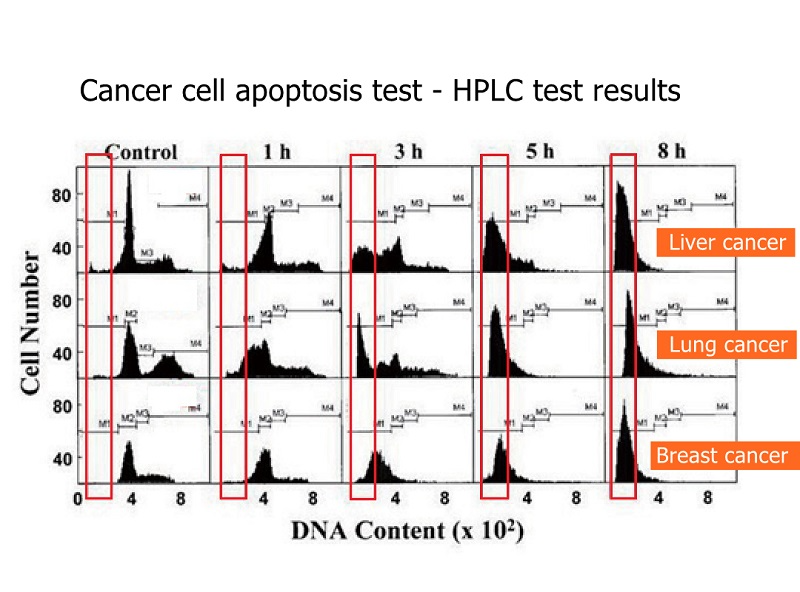
The figure shows that cancer cells can cause death.
The figure shows that the death of lung cancer cells is relatively slow, and it will not be obvious until eight hours later.
The figure shows that the death of liver cancer cells is very obvious, even more obvious in eight hours.
The graph shows that breast cancer cells die faster. It was obvious from the beginning that breast cancer is easy to treat, and patients with breast cancer need not worry.
Best Chemotherapy Adjuvant (1+1>487%)
Effectively improve chemotherapy effect and treatment.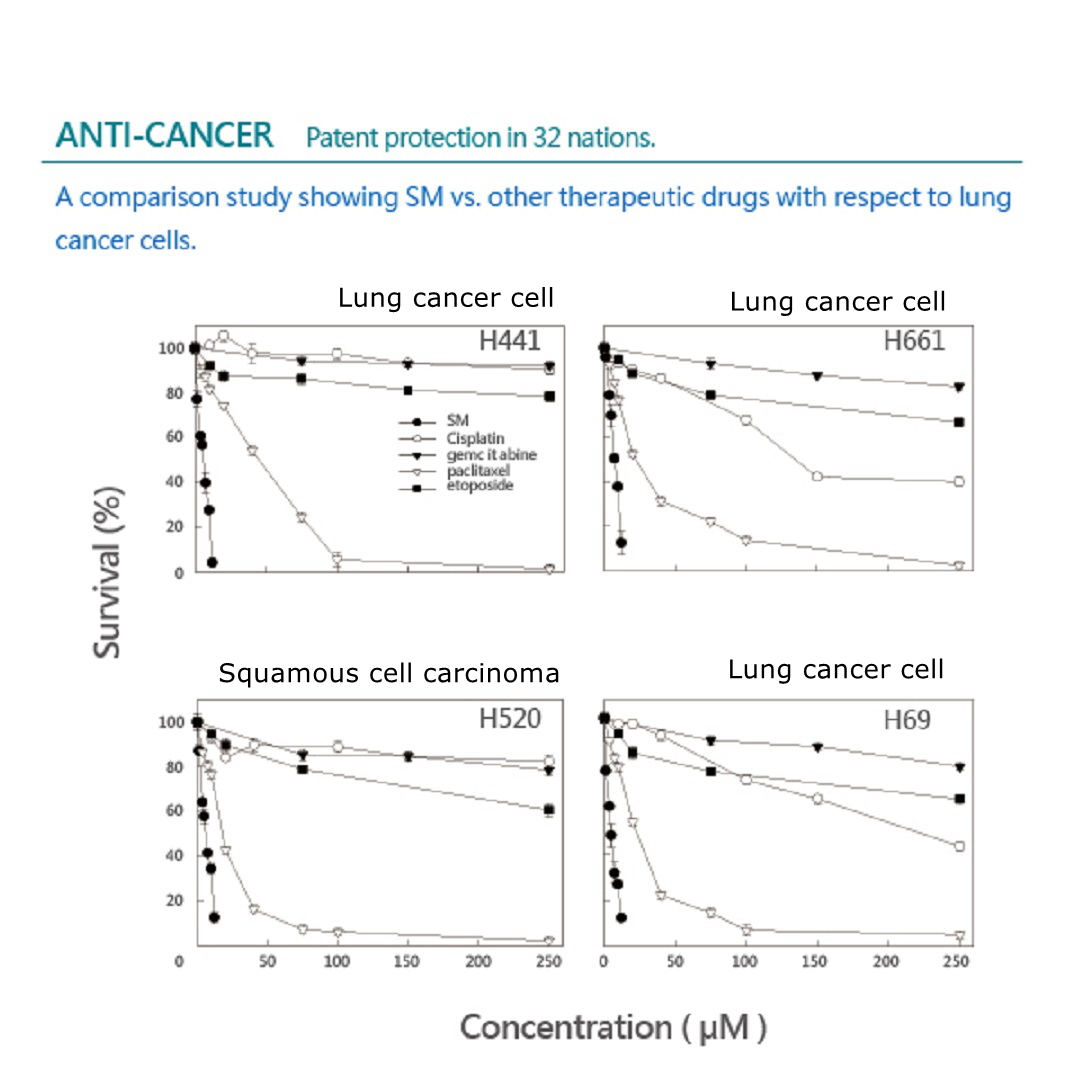
ANTI-CANCER
Patent protection in 32 nations.
A comparison study showing Solamargine vs. other therapeutic drugs with respect to lung cancer cells.
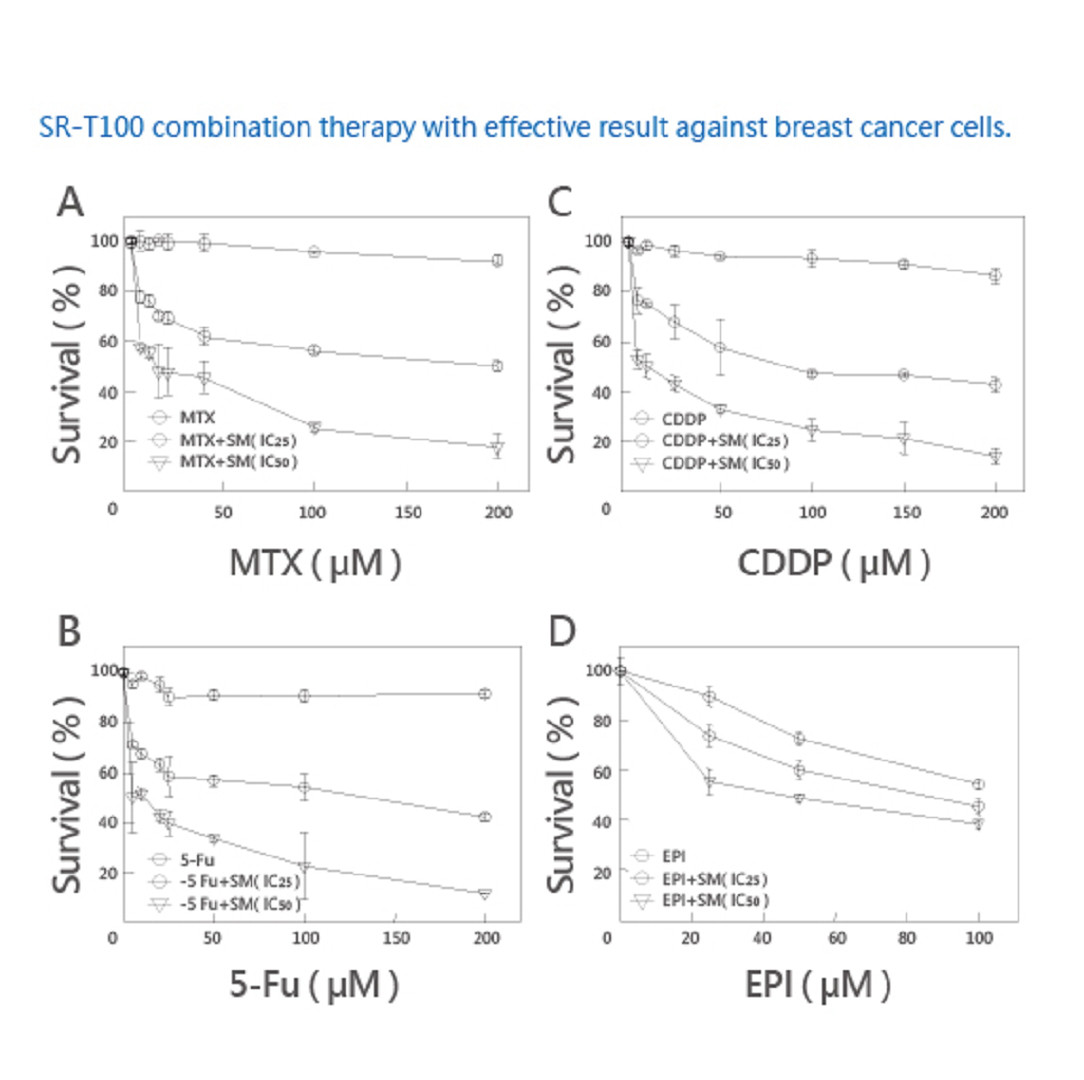
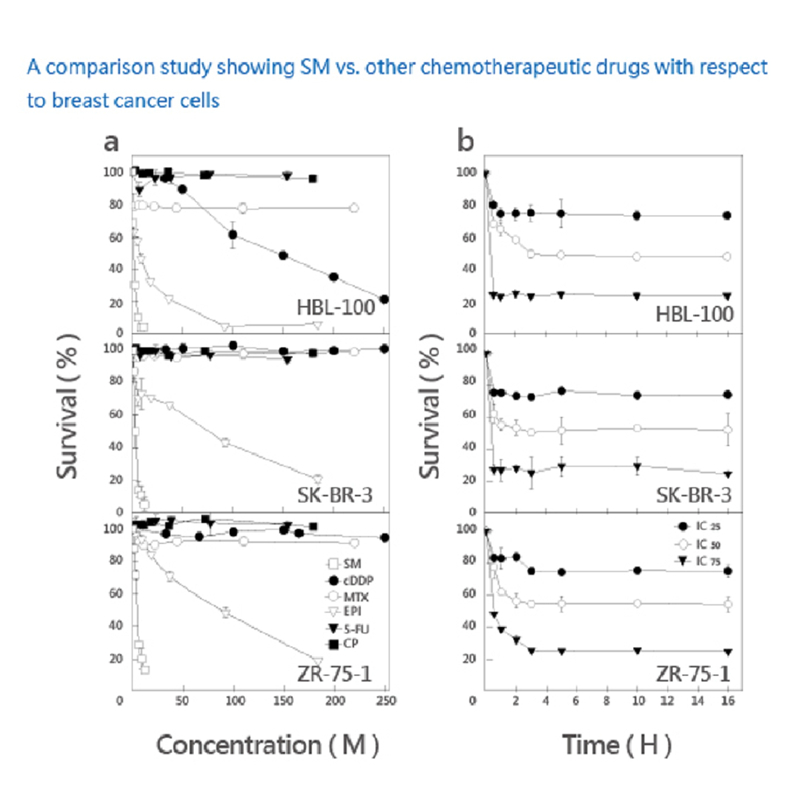 A comparison study showing Solamargine vs. other chemotherapeutic drugs with respect to breast cancer cells.
A comparison study showing Solamargine vs. other chemotherapeutic drugs with respect to breast cancer cells.
SR-T100 combination therapy with effective result against breast cancer cells.